Complete guide to Ratan Tata Road 41.5 km greenfield expressway connecting ORR to RRR. Phases, cost ₹4,030 crore, timeline, real estate impact & investment potential.
Introduction: A Game-Changing Infrastructure Development
The Government of Telangana has launched one of its most ambitious infrastructure initiatives in recent years the Ratan Tata Regional Ring Road, a 41.5-kilometer greenfield expressway designed to redefine connectivity in southern Hyderabad. With an estimated investment of over ₹4,030 crore, this project aims to reduce congestion, unlock new economic zones, and accelerate the growth of Hyderabad’s Future City corridor.
Named after the legendary industrialist Ratan Tata, the project reflects a long-term vision focused on sustainability, future-ready mobility, and inclusive development. More importantly, it represents a strategic link between Hyderabad’s two major ring roads, creating a seamless transportation backbone for the city’s next growth phase.
This guide explains the project in detail, covering its route, design, timeline, land acquisition, and its significant impact on real estate and economic development.
What Is the Ratan Tata Road?
Project Vision and Purpose
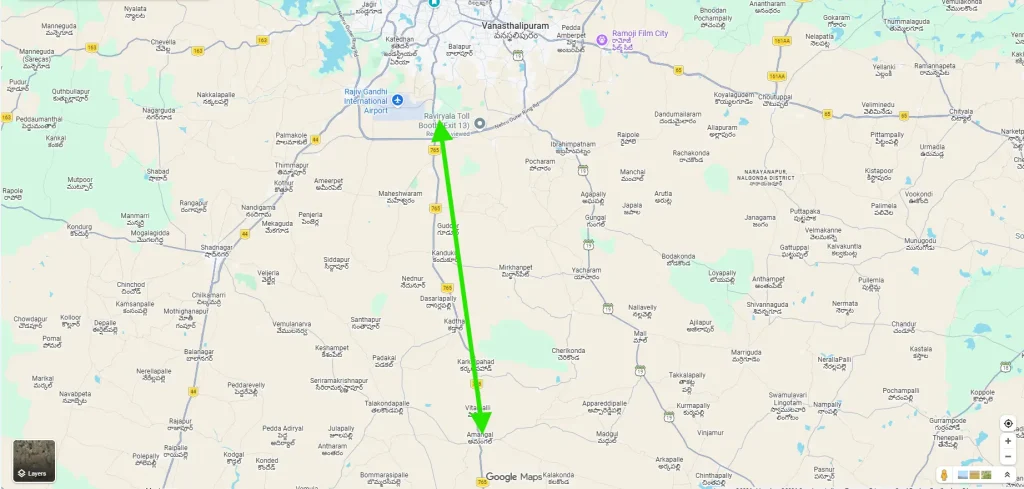
Officially known as Greenfield Radial Road–1 (GR-1), the Ratan Tata Road is an access-controlled, six-lane expressway planned with future expansion in mind. Unlike conventional highways, it is engineered as a next-generation urban expressway that integrates road, public transport, and utility infrastructure into a single corridor.
The expressway connects the Outer Ring Road at Raviryal to the Regional Ring Road at Amangal, passing through Hyderabad’s proposed Future City zone. As a result, it acts as a direct radial link between the metropolitan core and the wider regional network.
Why the Name “Ratan Tata Road”?
The Telangana government named this project in honor of Ratan Tata to symbolize visionary leadership and nation-building through infrastructure. His legacy of industrial development, ethical governance, and long-term planning aligns closely with the intent behind this expressway.
Strategic Route and Areas Covered
Key Connectivity Points
The 41.5 km alignment ensures uninterrupted, high-speed travel between major infrastructure nodes:
- Outer Ring Road (ORR) at Raviryal (Tata Interchange)
- Hyderabad Future City development zone
- Regional Ring Road (RRR) at Amangal
This configuration significantly improves north–south and regional connectivity while decongesting existing arterial roads.
Mandals and Villages Impacted
The expressway passes through 14 villages across six mandals in Rangareddy district:
Mandals Covered
- Maheshwaram
- Ibrahimpatnam
- Kandukur
- Yacharam
- Kadthal
- Amangal
Approximately 1,003 acres of land are involved. While these areas were largely semi-rural, the project is expected to convert them into organized urban and industrial corridors, creating new livelihood opportunities.
Project Phases and Investment Structure
Two-Phase Construction Plan
To ensure efficient execution, the project is divided into two phases:
Phase I: Raviryal to Meerkhanpet
- Length: 19.2 km
- Cost: ₹1,665 crore
Phase II: Meerkhanpet to Amangal
- Length: 22.3 km
- Cost: ₹2,365 crore
The combined investment, including land acquisition, is estimated between ₹4,030 and ₹4,621 crore.
Design Features and Infrastructure Specifications
Width and Lane Configuration
The expressway is being developed with a 100-meter right-of-way, which is wider than the existing ORR. Initially, it will operate as a six-lane access-controlled road, with provisions to expand to eight lanes in the future.
Central Median for Future Metro or Rail
A standout feature is the 20-meter central median, reserved exclusively for future Metro or rail corridors. Because of this forward-looking approach, the project avoids costly land acquisition and disruption later while supporting multimodal transport.
Sustainable and Inclusive Infrastructure
The design incorporates several people- and environment-friendly elements:
- Service roads on both sides for local traffic
- 2-meter-wide green belts for ecological balance
- 3-meter-wide cycle tracks promoting non-motorized transport
- 2-meter-wide footpaths ensuring pedestrian safety
- Dedicated utility corridors for water, power, telecom, and smart-city systems
Project Management and Timeline
Implementing Authorities
The project is being executed under the leadership of the Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority, with financial and operational support from Hyderabad Growth Corridor Limited (HGCL).
Construction Schedule
- Foundation stone laid on September 28, 2025, by Revanth Reddy
- Construction period: approximately 30 months
- Expected completion: 2028–2029
Land Acquisition and Compensation
The government is acquiring land in multiple tranches across all six mandals. To address concerns arising from earlier projects, authorities have adopted a transparent and consultative approach.
The proposed compensation stands at approximately ₹25 lakh per acre, along with rehabilitation measures and skill-development support to help affected farmers transition into new economic activities.
Connectivity Benefits and Travel Time Reduction
Once operational, the Ratan Tata Road will significantly alter travel patterns:
- Direct ORR–RRR connectivity
- Estimated 40–50% reduction in travel time
- Decongestion of southern Hyderabad roads
- Faster logistics movement for industries and exporters
As a result, both daily commuters and freight operators will benefit from predictable and efficient travel.
Real Estate Growth and Investment Impact
High-Growth Zones Along the Corridor
The expressway is expected to trigger rapid appreciation across multiple mandals:
- Maheshwaram: Emerging residential and industrial hotspot
- Ibrahimpatnam: New mixed-use developments
- Kandukur and Kadthal: Industrial and logistics hubs
- Yacharam and Amangal: Warehousing and future townships
Why Real Estate Demand Will Rise
Improved accessibility attracts developers, industries, and institutions. Consequently, residential projects, logistics parks, educational campuses, and healthcare facilities are likely to expand rapidly along the corridor.
Role in Hyderabad Future City Development
The Ratan Tata Road serves as the primary access spine for Hyderabad Future City. With seamless links to ORR, RRR, and the international airport, it positions Future City as a self-sustained urban zone featuring IT parks, residential communities, and commercial districts.
Industrial Growth and Employment Generation
Industrial and Logistics Enablement
The expressway supports large-scale industrial development, including manufacturing, electronics, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and e-commerce logistics.
Employment Potential
- Thousands of jobs during the construction phase
- Long-term employment in manufacturing, logistics, real estate, retail, and services
- Indirect job creation through ancillary industries
Sustainability and Smart Infrastructure
Environmental considerations are embedded throughout the project. Green belts, efficient drainage, and provisions for public transport help reduce carbon emissions. Furthermore, utility corridors enable smart-city features such as traffic monitoring, smart lighting, and high-speed digital connectivity.
Long-Term Economic Impact
Economists estimate a strong multiplier effect, with every rupee invested generating ₹2.5–₹3 in regional economic activity. Over time, the corridor is expected to attract investments worth tens of thousands of crores while significantly increasing state revenue.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Hyderabad
The Ratan Tata Regional Ring Road is more than an expressway it is a catalyst for transformation. By connecting ORR and RRR through Future City, it reshapes southern Hyderabad into a high-growth economic corridor.
With its future-ready design, sustainable planning, and strong real estate potential, the project stands as a landmark initiative in Telangana’s infrastructure journey. For investors, businesses, and residents alike, the Ratan Tata Road represents a decisive step toward Hyderabad’s next phase of growth.

